Abstract
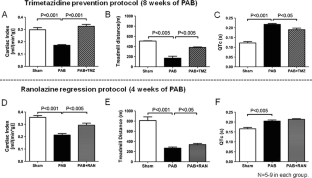
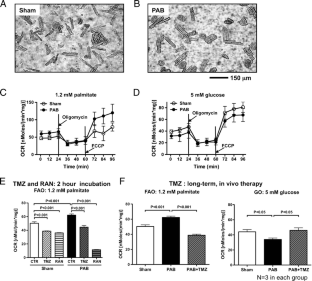
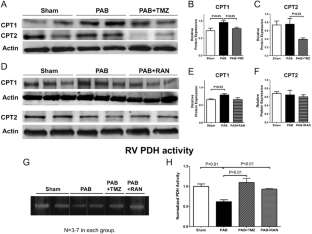
右心室肥大(RVH)和房车失败are major determinants of prognosis in pulmonary hypertension and congenital heart disease. In RVH, there is a metabolic shift from glucose oxidation (GO) to glycolysis. Directly increasing GO improves RV function, demonstrating the susceptibility of RVH to metabolic intervention. However, the effects of RVH on fatty acid oxidation (FAO), the main energy source in adult myocardium, are unknown. We hypothesized that partial inhibitors of FAO (pFOXi) would indirectly increase GO and improve RV function by exploiting the reciprocal relationship between FAO and GO (Randle’s cycle). RVH was induced in adult Sprague-Dawley rats by pulmonary artery banding (PAB). pFOXi were administered orally to prevent (trimetazidine, 0.7 g/L for 8 weeks) or regress (ranolazine 20 mg/day or trimetazidine for 1 week, beginning 3 weeks post-PAB) RVH. Metabolic, hemodynamic, molecular, electrophysiologic, and functional comparisons with sham rats were performed 4 or 8 weeks post-PAB. Metabolism was quantified in RV working hearts, using a dual-isotope technique, and in isolated RV myocytes, using a Seahorse Analyzer. PAB-induced RVH did not cause death but reduced cardiac output and treadmill walking distance and elevated plasma epinephrine levels. Increased RV FAO in PAB was accompanied by increased carnitine palmitoyltransferase expression; conversely, GO and pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) activity were decreased. pFOXi decreased FAO and restored PDH activity and GO in PAB, thereby increasing ATP levels. pFOXi reduced the elevated RV glycogen levels in RVH. Trimetazidine and ranolazine increased cardiac output and exercise capacity and attenuated exertional lactic acidemia in PAB. RV monophasic action potential duration and QTc interval prolongation in RVH normalized with trimetazidine. pFOXi also decreased the mild RV fibrosis seen in PAB. Maladaptive increases in FAO reduce RV function in PAB-induced RVH. pFOXi inhibit FAO, which increases GO and enhances RV function. Trimetazidine and ranolazine have therapeutic potential in RVH.
这是订阅内容的预览access via your institution。





References
- 1。
Rajabi M,Kassiotis C,Razeghi P,Taegtmeyer H(2007)返回胎儿基因程序保护了压力的心脏:一个强烈的假设。Heart Fail Rev 12:331–343
- 2。
Bogaard HJ,Natarajan R,Henderson SC,Long CS,Kraskauskas D,Smithson L,Ockaili R,McCord JM,Voelkel NF(2009)慢性肺动脉压力升高是不足以解释正确的心力衰竭。流通120:1951–1960
- 3。
Piao L, Fang YH, Cadete VJ, Wietholt C, Urboniene D, Toth PT, Marsboom G, Zhang HJ, Haber I, Rehman J et al (2010) The inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase improves impaired cardiac function and electrical remodeling in two models of right ventricular hypertrophy: resuscitating the hibernating right ventricle. J Mol Med 88:47–60
- 4。
Oikawa M, Kagaya Y, Otani H, Sakuma M, Demachi J, Suzuki J, Takahashi T, Nawata J, Ido T, Watanabe J et al (2005) Increased [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose accumulation in right ventricular free wall in patients with pulmonary hypertension and the effect of epoprostenol. J Am Coll Cardiol 45:1849–1855
- 5。
Rich S,Pogoriler J,Husain AN,Toth PT,Gomberg-Maitland M,Archer SL(2010年),雌酮酚对特发性肺动脉高压的长期影响。胸部138:1234–1239
- 6。
Stanley WC,Lopaschuk GD,Hall JL,McCormack JG(1997)在正常和缺血性条件下调节心肌碳水化合物代谢。药理干预措施的潜力。Cardiovasc Res 33:243–257
- 7。
Randle PJ, Priestman DA, Mistry SC, Halsall A (1994) Glucose fatty acid interactions and the regulation of glucose disposal. J Cell Biochem 55(Suppl):1–11
- 8。
Abozguia K,Clarke K,Lee L,Frenneaux M(2006)修饰心肌底物用作心力衰竭的疗法。Nat Clin练习Cardiovasc Med 3:490–498
- 9.
Gunes Y, Guntekin U, Tuncer M, Sahin M (2009) Improved left and right ventricular functions with trimetazidine in patients with heart failure: a tissue Doppler study. Hear Vessel 24:277–282
- 10。
Kantor PF,Lucien A,Kozak R,Lopaschuk GD(2000年)抗统治药物三翼胺将心能代谢从脂肪酸氧化转移到葡萄糖氧化,通过抑制线粒体长链3-酮乙酰乙酰酰基辅酶A硫醇酶。Circ Res 86:580–588
- 11。
McClellan KJ,Plosker GL(1999)Trimetazidine。综述其在稳定的心绞痛和其他冠状动脉疾病中的使用。毒品58:143–157
- 12。
Meng D,Feng L,Chen XJ,Yang D,Zhang JN(2006)Trimetazidine改进了Ca2+handling in isoprenaline-mediated myocardial injury of rats. Exp Physiol 91:591–601
- 13。
Guarnieri C,Muscari C(1990)三唑胺对心肌中线粒体功能和超氧化物产生的有益作用。Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 4(补充4):814–815
- 14。
Wang P,Fraser H,Lloyd SG,McVeigh JJ,Belardinelli L,Chatham JC(2007)Ranolazine和CVT-4325的比较,一种新型的脂肪酸氧化抑制剂,这是对心脏代谢的脂肪酸氧化的一种新型抑制剂,以及在Rative falcularist of Cartiac代谢和左心室功能中的比较。缺血和再灌注。J Pharmacol Exp Ther 321:213–220
- 15。
Stanley WC(2002)稳定心绞痛的部分脂肪酸氧化抑制剂。专家OPIN调查药物11:615–629
- 16。
Fragasso G, Spoladore R, Cuko A, Palloshi A (2007) Modulation of fatty acids oxidation in heart failure by selective pharmacological inhibition of 3-ketoacyl coenzyme-A thiolase. Curr Clin Pharmacol 2:190–196
- 17。
Samudio I, Harmancey R, Fiegl M, Kantarjian H, Konopleva M, Korchin B, Kaluarachchi K, Bornmann W, Duvvuri S, Taegtmeyer H et al (2010) Pharmacologic inhibition of fatty acid oxidation sensitizes human leukemia cells to apoptosis induction. J Clin Invest 120:142–156
- 18。
McCormack JG, Barr RL, Wolff AA, Lopaschuk GD (1996) Ranolazine stimulates glucose oxidation in normoxic, ischemic, and reperfused ischemic rat hearts. Circulation 93:135–142
- 19。
Clarke B,Wyatt KM,McCormack JG(1996)Ranolazine在灌注型常氧大鼠心脏中增加了活性丙酮酸脱氢酶:间接机制的证据。J Mol细胞Cardiol 28:341–350
- 20。
Fraser H, Belardinelli L, Wang L, Light PE, McVeigh JJ, Clanachan AS (2006) Ranolazine decreases diastolic calcium accumulation caused by ATX-II or ischemia in rat hearts. J Mol Cell Cardiol 41:1031–1038
- 21。
Undrovinas AI, Belardinelli L, Undrovinas NA, Sabbah HN (2006) Ranolazine improves abnormal repolarization and contraction in left ventricular myocytes of dogs with heart failure by inhibiting late sodium current. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 17(Suppl 1):S169–S177
- 22。
Antzelevitch C, Belardinelli L, Zygmunt AC, Burashnikov A, Di Diego JM, Fish JM, Cordeiro JM, Thomas G (2004) Electrophysiological effects of ranolazine, a novel antianginal agent with antiarrhythmic properties. Circulation 110:904–910
- 23。
Sentex E,Helies-Toussaint C,Rousseau D,Lucien A,Ferrary E,Grynberg A(2001)三翼胺对心脏和其他靶器官中复杂脂质合成的影响。Indam Clin Pharmacol 15:255–264
- 24。
Lopaschuk GD, Spafford MA, Davies NJ, Wall SR (1990) Glucose and palmitate oxidation in isolated working rat hearts reperfused after a period of transient global ischemia. Circ Res 66:546–553
- 25。
Tuunanen H, Engblom E, Naum A, Nagren K, Scheinin M, Hesse B, Juhani Airaksinen KE, Nuutila P, Iozzo P et al (2008) Trimetazidine, a metabolic modulator, has cardiac and extracardiac benefits in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation 118:1250–1258
- 26。
Tabbi-Anneni I,Helies-toussaint C,Morin D,Bescond-Jacquet A,Lucien A,Grynberg A(2003)通过Trimetazidine治疗预防大鼠的心力衰竭:导致磷脂交换的结果?J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304:1003–1009
- 27。
Guarnieri C, Muscari C (1988) Beneficial effects of trimetazidine on mitochondrial function and superoxide production in the cardiac muscle of monocrotaline-treated rats. Biochem Pharmacol 37:4685–4688
- 28。
Piao L,Marsboom G,Archer SL(2010)右心肥大和衰竭中的线粒体代谢适应。J Mol Med 88:1011–1020
- 29。
Wilson SR,Scirica BM,Braunwald E,Murphy SA,Karwatowska-Prokopczuk E,Buros JL,Chaitman BR,Morrow DA(2009)Ranolazine在随机,双盲,安慰剂,安慰剂中,慢性心脏病观察患者中的疗效TIMI(雷诺嗪的代谢效率减少了非ST段升高急性冠状动脉综合征的缺血)36试验。J Am Coll Cardiol 53:1510–1516
致谢
Archer博士得到NIH-RO1-HL071115和1RC1HL099462-01的支持,以及美国心脏协会(AHA)。
披露
None.
作者信息
Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
以下是电子补充材料的链接。
ESM 1
(PDF 157 kb)
权利和权限
关于这篇文章
Cite this article
Fang,YH。,Piao,L.,Hong,Z。等。右心肥大中脂肪酸氧化的治疗性抑制:exploiting Randle’s cycle。J Mol Med90,31-43(2012)。https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0804-9
Received:
修改:
公认:
出版:
Issue Date:
关键字
- Pulmonic stenosis
- 单相动作潜在持续时间
- QTc interval
- 心肌纤维化
- Right heart failure
